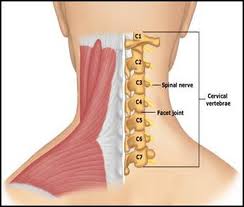
What is Neck Pain?
Our neck is subjected to stress, strain and minor injury on daily and ongoing basis. Over time this result in the degeneration of our cervical spine, causing neck pain. This occurs anywhere from the bottom of our head to the top of our shoulders and may radiate to our upper back and arms. This area basically supports all the load of our head. The pain restricts the movement of our head and neck. How quick our neck pain recovers and whether it will develop into chronic neck pain will depend on the overall condition of our cervical spine.
Older people are more prone to neck pain and in most cases the condition will disappear. Others will need to consult the doctor and receive appropriate treatment.
Structure of the Neck
Our neck consists of the cervical spine and the soft tissues that surround it. The soft tissues include nerves, ligaments, tendons, muscles and blood vessels. The cervical spine is located just below our skull and ends just above our thoracic spine. Our cervical spine is made up of the first seven vertebrae in the spine, C1 through C7.
Symptoms of Neck Pain
- Stiffness and reduced range of motion in your neck
- Pain in your shoulders and arms
- Inability to touch your chin to your chest
- Headaches
- Dizziness
- Numbness, tingling, tenderness, sharp piercing pain
- Difficulty in swallowing
- Lights hurt your eyes
- Weakness in your legs
In serious cases, symptoms include fever, vomiting, severe headache, and you should seek emergency treatment.
Sometimes neck pain is accompanied by upper back and/or lower back pain due to inflammation of the spine. Acute neck pain may force the head to turn to one side, a condition known as torticollis.
How to Diagnose Neck Pain
To understand what causes your neck pain, the doctor would normally check your medical history follow by a thorough physical examination. This will provide a good basis for the doctor to assess the reasons for your neck pain. However to be sure of what are the actual causes of your neck pain, one or more of several diagnostic tests may have to be conducted, including:
- X-rays
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
- CAT Scan (Computer Assisted Tomography)
- Myelography (a special x-ray sensitive contrast dye is injected to illuminate the spine, allowing identification of problems within the spine)
- Electromyogram (EMG)
- Bone Scan
- Laboratory tests
Causes of Neck Pain
There are many causes of neck pain including daily activities requiring repeated use of the neck, injuries and diseases.
Neck pain caused by activities resulting in strained muscles, sprained ligament or inflammation of joints:
- Improper sleeping posture including on a pillow that doesn’t support your head or on your stomach with neck twisted.
- Maintaining a prolonged awkward working your computer, painting the ceiling or installing a light bulb
- Tilting your head in a fixed position like talking on the phone or reading a book in bed
- Laying on your sofa watching TV for hours
- Carrying heavy loads on your shoulders or with hands
- Hunching your upper body during long distance driving
Neck pain caused by injuries
Our neck is very vulnerable to injury because it is so flexible and bears the whole weight of our head. Injuries include:
- Whiplash when the head is jerked forward and then backward in a car accident
- Falling or tripping
- Injuries related to sporting activities, especially those involving head and upper body
- Knocks and blows to the face or head.
Neck pain caused by medical conditions including:
- Rheumatoid arthritis (inflammation of the joints and surrounding tissues)
- Cervical spinal stenosis (narrowing of the spinal canal)
- Meningitis (swelling of the brain lining and spinal cord)
- Cancer (tumours in the spine)
- Fibromyalgia (long-term, body-wide pain and tenderness in the joints, muscles, tendons, and other soft tissues)
- Ruptured disk
- Minor fractures to the spine from osteoporosis
- Spondylosis (degenerative disorder of the spine)
- Flu
Treatment and Prevention of Neck Pain
Treatment for neck pain generally falls into two main categories: conservative treatment (non-surgical) and surgical treatment. The objectives of the treatments are to relieve the pain and reduce the risk of injury again.
Non-Surgical Treatment for Your Neck Pain
Medications
- Muscle relaxants, tramadol (Ultram) or tricyclic antidepressant medications used for pain
- Opioid analgesics
- Injection of corticosteroid or numbing medications (lidocaine) into the muscles in your neck.
Some medications are very addictive. Take them exactly as prescribed and see your doctor if you feel unwell or have other side effects.
Physical Therapy
Your physiotherapist can design an exercise program to help you recover from your neck pain and also teach you ways to prevent further injury to your neck.
Cervical Pillow
A cervical pillow provides good support to your head and neck which helps to reduce stress to your spine.
Cervical Collar
A cervical collar provides support to your injured neck and limit motion while it is healing. It also helps keep your body in the normal alignment.
Epidural Steroid Injection (ESI)
his is normally used only when other non-surgical treatments fail to relieve your neck pain. In this process a small amount of cortisone, a strong anti-inflammatory medicine, is injected into the bony spinal canal.
Complementary and alternative treatments
Some of these treatments are helpful in relieving pain, restore neck mobility and improve quality of life.
- Massage
- Chiropractic and osteopathic treatments
- Yoga helps improve flexibility, posture and breathing, decrease stress, and maintain health
- Acupuncture
- Heat or ice treatment
- Take warm showers
Surgical Treatment
Surgery is normally the last option and your doctor will recommend what works best for you.
Discectomy
This procedure relieves the pressure on a nerve root by removing the herniated disc causing the pressure.
Cervical Fusion
This procedure joins selected bones in the neck with bones taken from other parts of your body. The bone graft between two or more vertebrae allows them to fuse and grow together.
Posterior Fusion
In this case the bone graft is placed on the back side of the vertebrae. This allows the vertebrae to grow together, creating a solid piece of bone out of the two vertebrae. This procedure is generally used only for fractures of the spine.
Instrumented Cervical Fusion
To improve fusion, metal plates, screws, and rods that hold the spine in place are introduced. As the bones are tightly held and there is less motion, it will help the healing process.
Laminectomy
This is a spine operationto remove the portion of the vertebral bone called the lamina. This procedure reduces the pressure on the spinal cord and the irritation and inflammation of the spinal nerves.
Corpectomy and Strut Graft
This is a procedure that involves removing part of the vertebral body as a way to decompress the spinal cord and nerves.
Surgeries associated with the spine are normally risky and may lead to complications. You should discuss with your medical professionals on the various options and consequences before deciding on which is the best option.
Surgery is normally the last option and your doctor will recommend what works best for you.
Prevention of neck pain
Neck pain causes can be reduced by adopting good and new habits.
Refrain from spending a lot of time in positions that stress and strain your neck. Among others things, these include sitting at a computer for extended periods.
Take short breaks in between work several times a day. Sleep on a firm pillow with good support for your neck. Do not sleep on your stomach in an awkward position. If you really have to read a book in bed make you keep your neck in a neutral position. Stop smoking because it decreases blood supply and slow down tissue repair and healing.
Develop a habit of exercising regularly as it is good for the long term health of your body. Best of all, unlike medication and surgery, it is virtually free.